ISO27002:2022 – what’s new?
| Joost Krapels |
Security

ISO 27001:2013, a certification standard for Information Security Management systems, uses an extensive list of example control measures that organisations have to comply with, or explain the control is not applicable (comply or explain). This list of 114 controls is elaborated on in ISO 27002, showing how to implement them in practice. After eight years, ISO 27002 is about to be updated. In this article we give a short overview of the changes.
First and foremost, take note that the newest version of ISO 27002 has not yet been adopted by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). It is possible, though unlikely, that controls might change. The process is now in the approval stage, and you can follow it on the ISO website.
Note 01-2023: ISO 27001:2022 is now officially published. Only some minor changes were done.
ISO 27002 is not a standard you can certify against, but ISO 27001 is. ISO 27002 elaborates on the example control measures mentioned in the appendix of ISO 27001. Since there is no ISO 27001:2022 yet, organisations already certified for, in the process of implementing, or planning to get certified for ISO 27001 in the next year should stick to the appendix of ISO 27001:2013. Only when ISO 27001 is updated and references ISO 27002:2022, should you start using the new list of controls.
Changes in structure
Chapters
The example controls in ISO 27002:2013 were categorized in fourteen chapters: chapters 5-18. The new ISO27002 slims this down to only four chapters: five through eight. Just like the 2013 version, not all chapters are created equal:
- Ch5, Organizational controls, contains 37 controls
- Ch6, People controls, contains 8 controls
- Ch7, Physical controls, contains 14 controls
- Ch8, Technological controls, contains 34 controls
This brings the total to 93 controls; roughly a 20% reduction.
Attributes
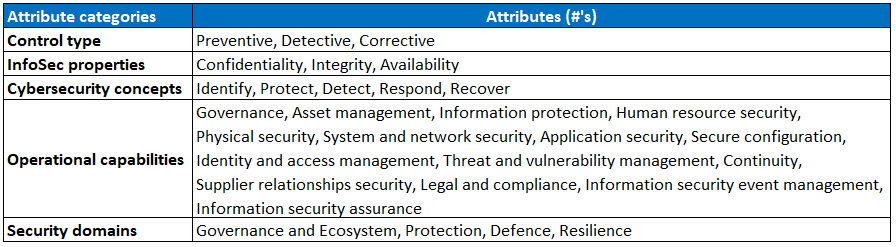
An interesting addition is the introduction of attributes, indicated by an hashtag (#). These attributes can be used to group together similar controls, but can also provide guidance where to place responsibility for those controls in your organization. ISO created five categories of attributes:
- Control type: When does the control have an effect?
- InfoSec properties: Which part(s) of the CIA triangle will be protected?
- Cybersecurity concepts: What type of (ISO 27101) action is taken?
- Operational capabilities: Which security specialization(s) does the control belong to?
- Security domains: Which information security work field is concerned?
Every single control is tagged with one or more of the following attributes per category:
Attributes are, therefore, not the same as descriptive subchapters in ISO 27001:2013. They can, however, serve a similar purpose.
New controls
In total, ISO 27002:2022 contains eleven new controls:
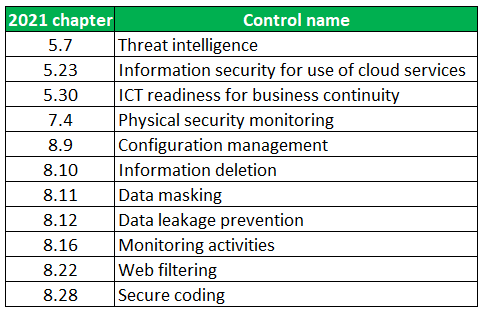 (Edit 01-2023: Web filtering has become 8.23 instead of 8.22)
(Edit 01-2023: Web filtering has become 8.23 instead of 8.22)
To us, threat intelligence and data masking stand out the most. The other topics are quite closely related to already existing ones, but collecting and analyzing information about the security threat landscape and the privacy by design principle of data masking are interesting new additions.
Changed controls
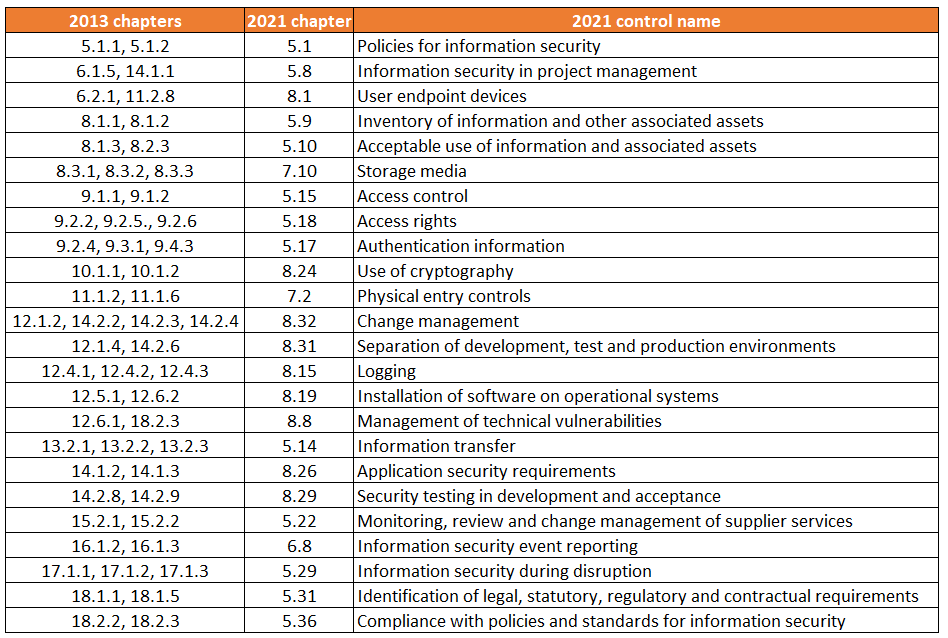
56 controls from 2013 have been merged into 24 controls:
Many chapters that were already quite similar have been consolidated. For example, the ISO 27002:2013 controls of Policy on the use of cryptographic controls (10.1.1) and Key management (10.1.2) are now simply Use of cryptography. Some compounds are chapter transcending, however, such as Change management from the chapter Operations security (12) with three system, application, and software change controls from System acquisition, development and maintenance (14).
Deleted controls
Only one control from the 2013 version has been deleted, Removal of assets. Since its sister control, Security of equipment and assets off-premises (11.2.6) already covers the protection of assets outside organizational boundaries, we think this change makes sense.
ISO 27002 explained
We wrote four articles on ISO 27002:2013, giving a short summary of all the controls:
- Pt1 on chapters five to eight
- Pt2 on chapters nine to eleven
- Pt3 on chapters twelve to fourteen
- Pt4 on chapters fifteen to eighteen
Of course we have covered the new version as well. You can find the four articles here:
- Pt1 on organizational controls
- Pt2 on people controls
- Pt3 on physical controls
- Pt4 on technological controls
Image credit: source image by @sincerelymedia via Unsplash, edited by ICT Institute
Joost Krapels has worked at ICT Institute from 2019 - oct 2024. He is a security and privacy officer with a lot of GDPR and ISO 27001 experience, and has Security+ and CISSP certification.